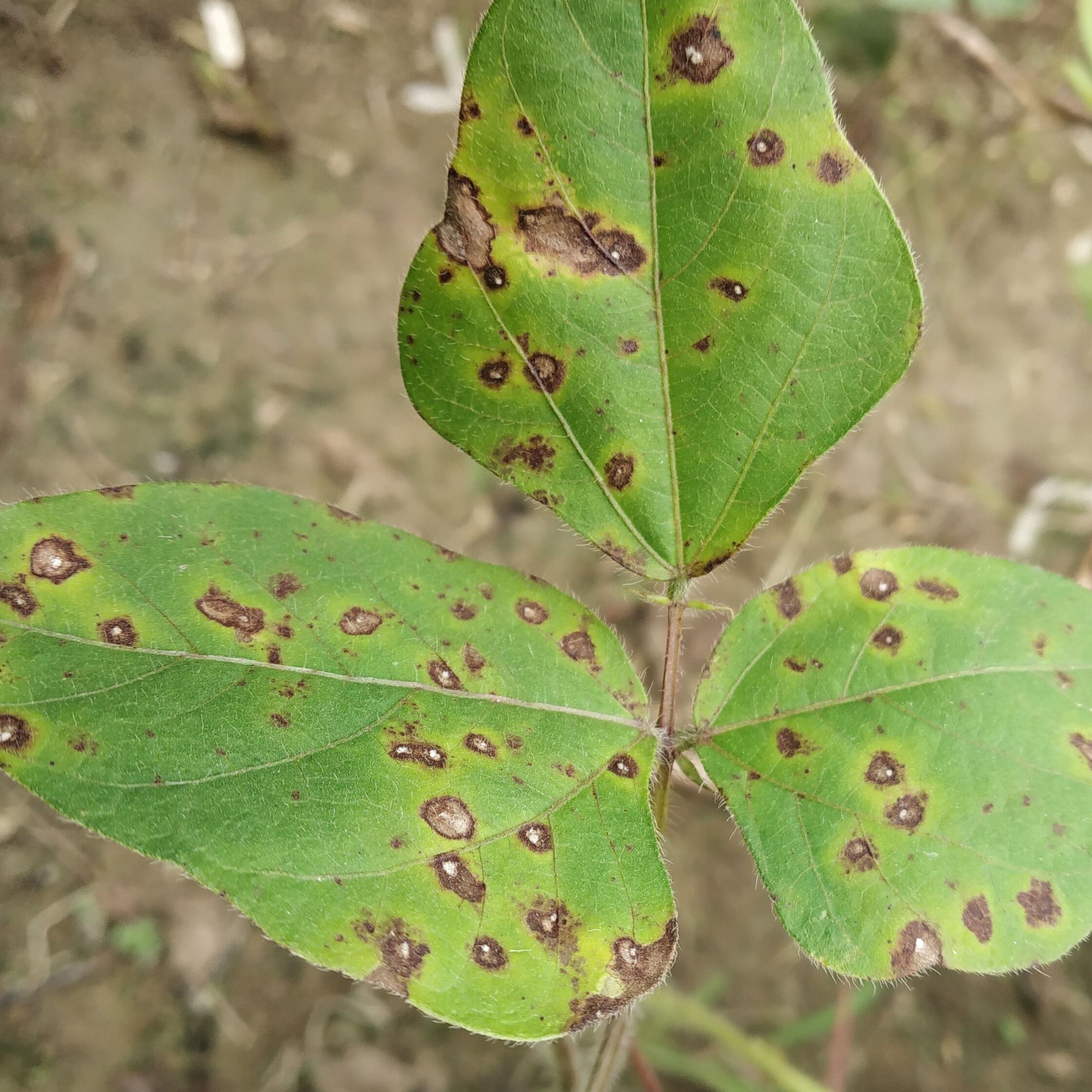
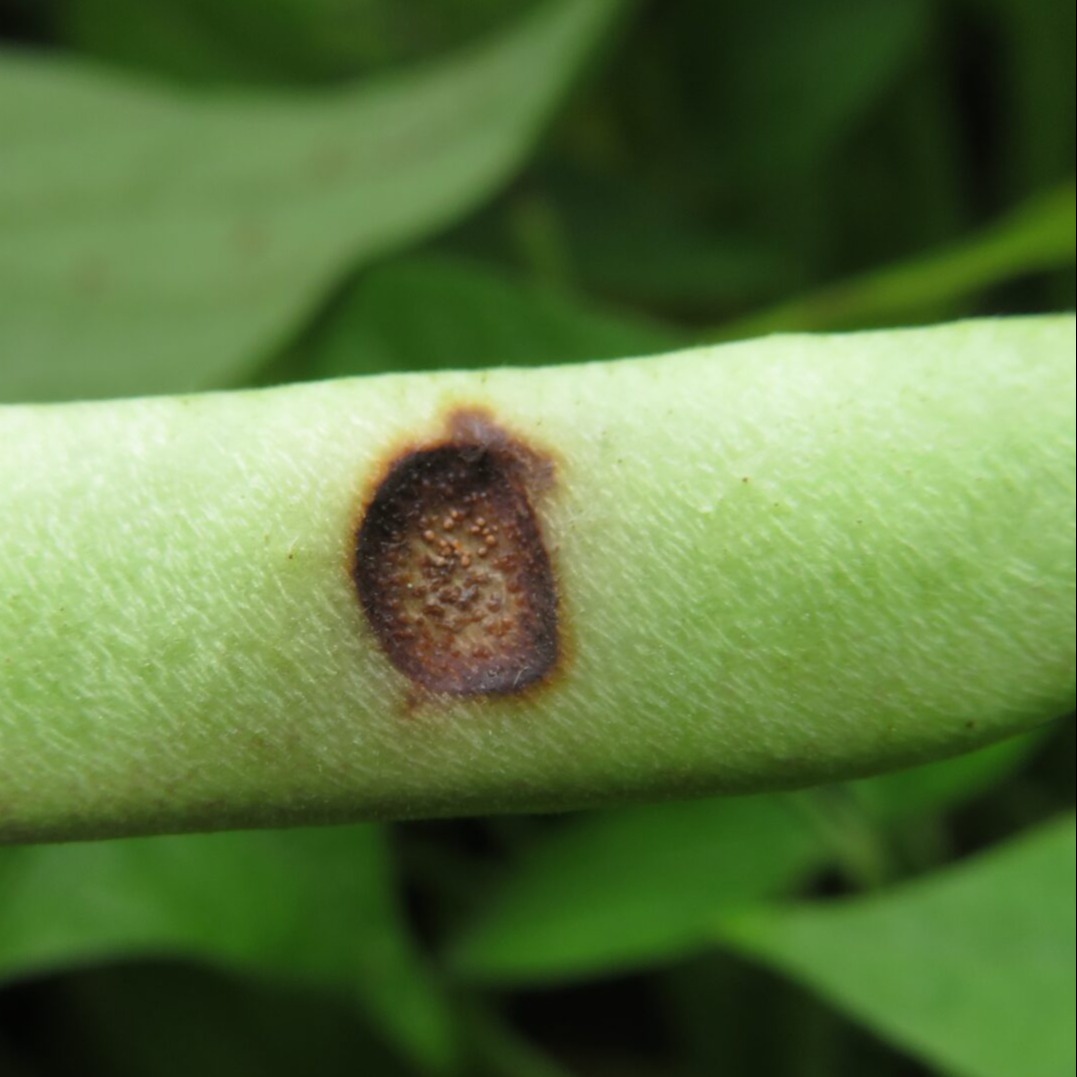
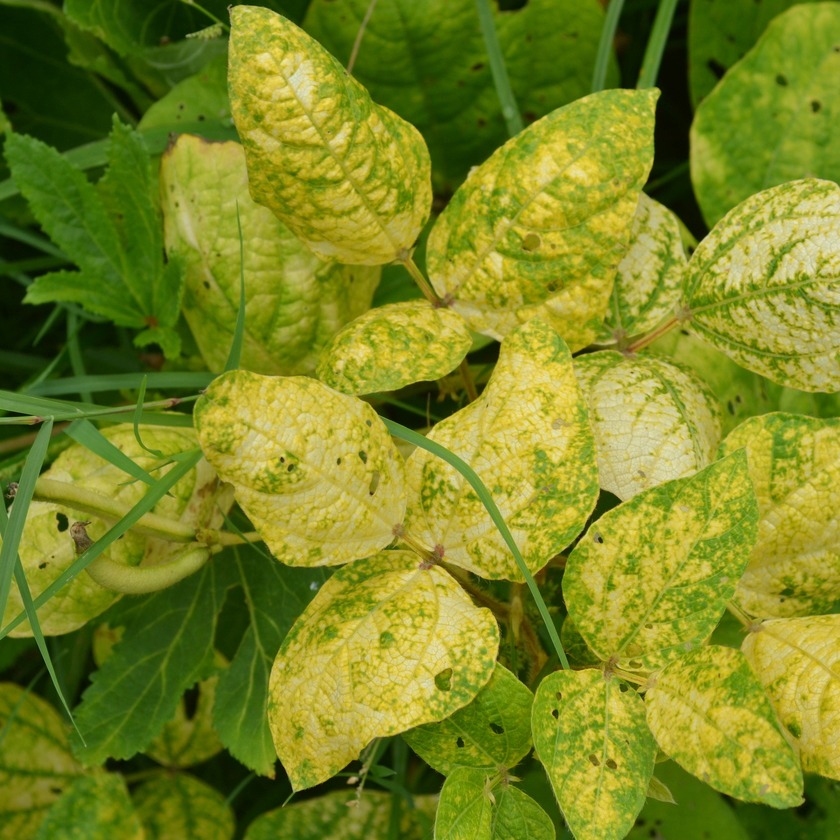
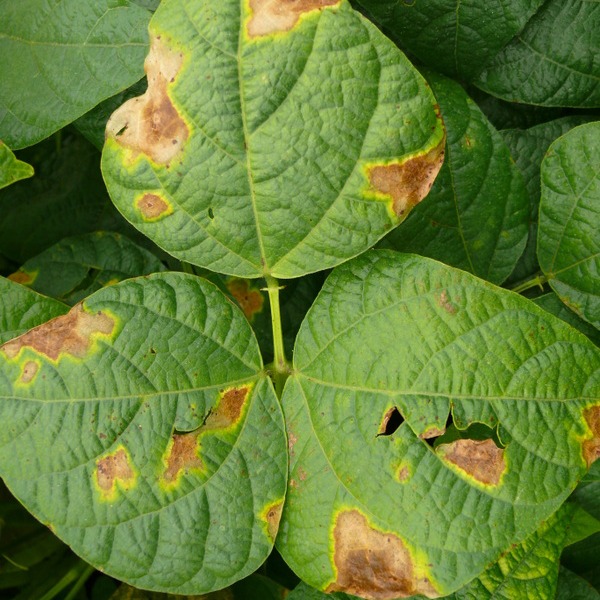
Dry root rot
Symptom
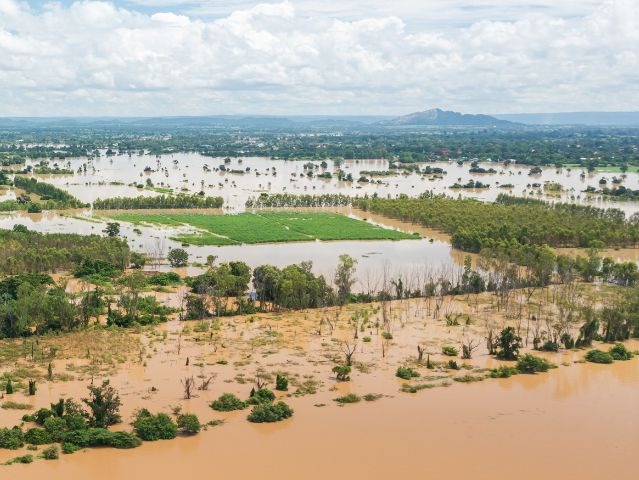
Rhizoctonia root rot, caused by the Rhizoctonia fungus, primarily affects plants during the flowering and fruiting stages. Infected fields exhibit scattered cases of plant wilting and desiccation. The upper leaves of affected plants droop, while the foliage and stems develop a straw-colored hue, with occasional brown discoloration on the lower leaves. Upon uprooting, infected plants often lack lateral roots, with only the primary taproot remaining. This disease is more prevalent in cooler seasons and is more commonly observed in sandy soils compared to clay soils.