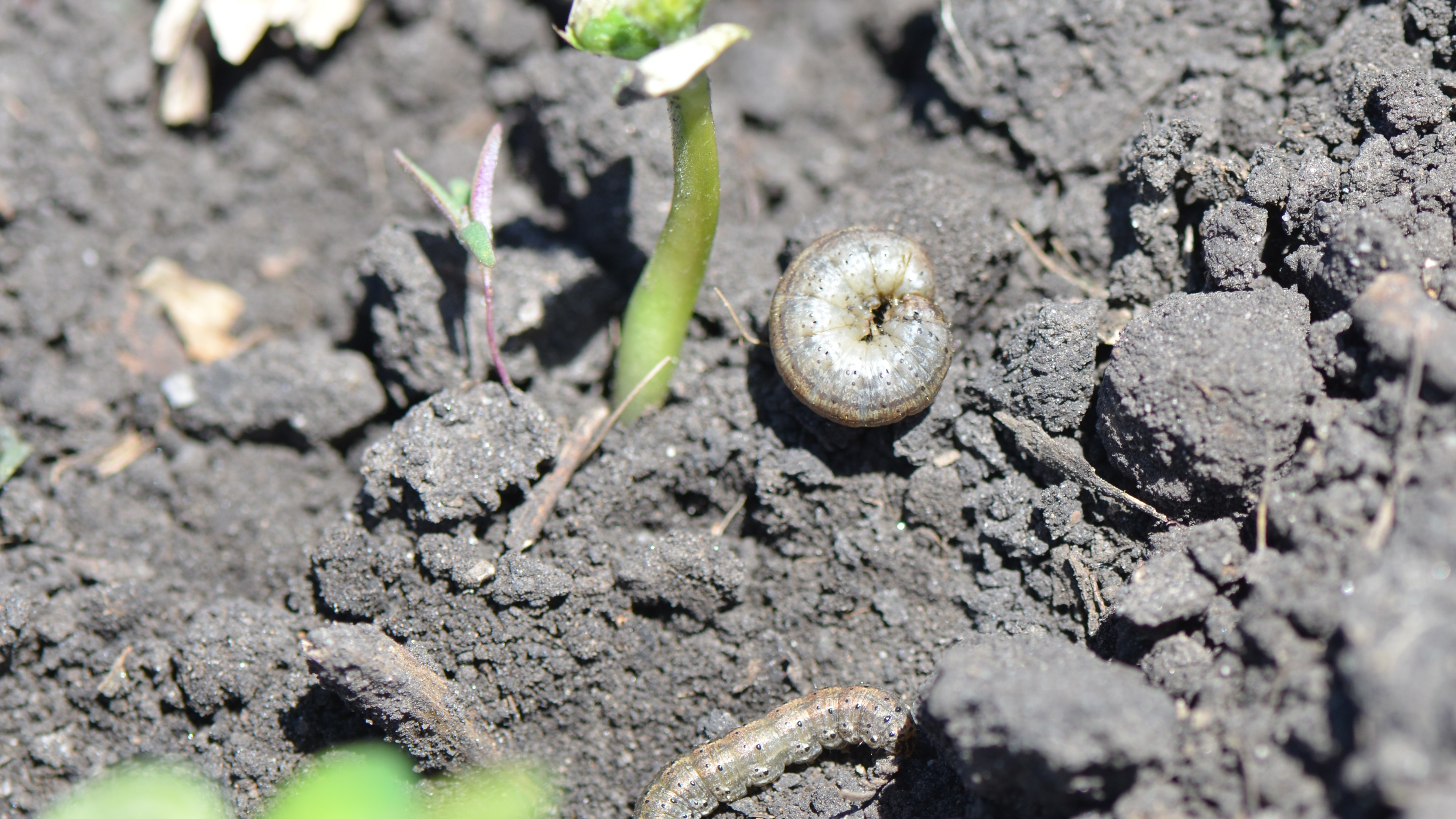
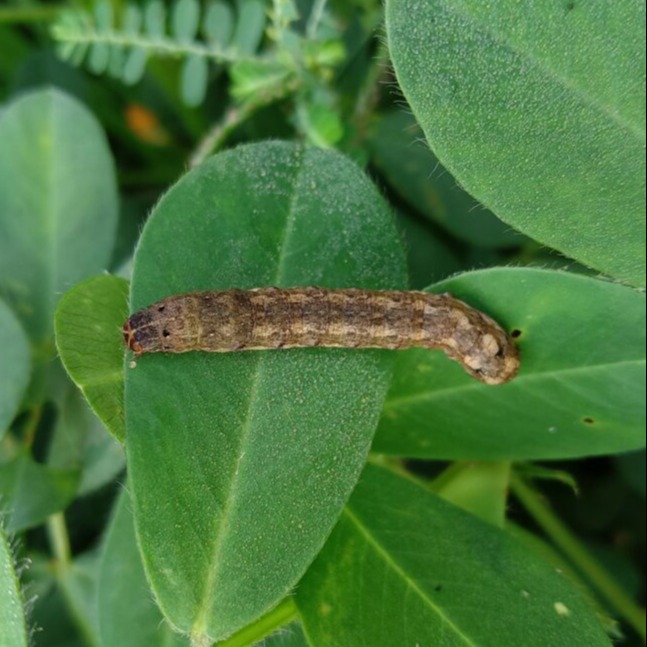
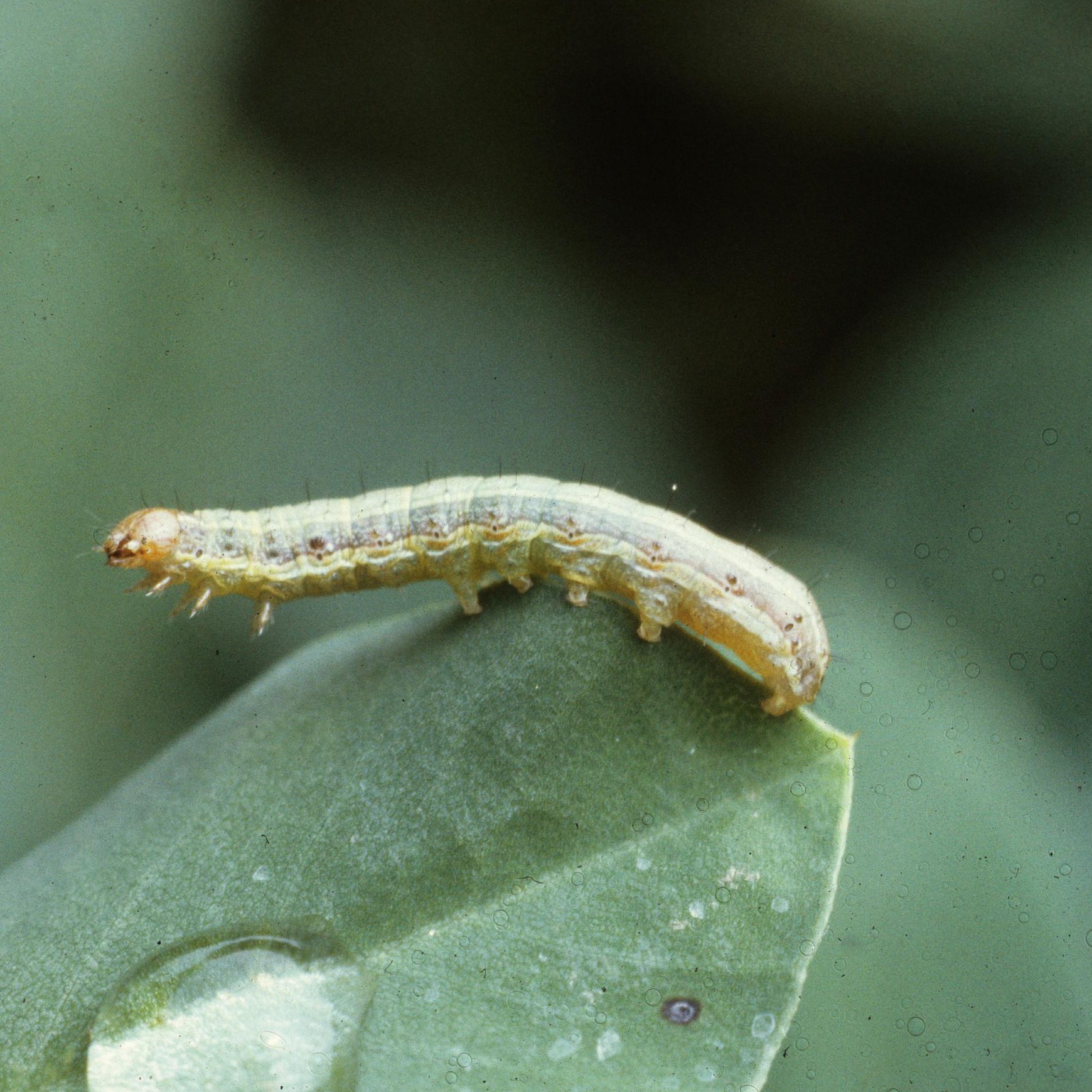
Common Cutworm
Symptom
Under dry conditions, the young larvae make short feeding visits to the foliage during the day and hide in the uppermost 1-3 mm of the soil for the rest of the time. External feeding on leaves by the first instar and second instar larvae results in the presence of very tiny round 'windowpanes' where the larvae have eaten away the upper epidermis and the green tissue, but left the lower epidermis. Third instar larvae begin to eat roots at the surface and exhibit negative phototaxis. This change in biology is reinforced in the fourth, fifth and sixth instars which feed voraciously on roots and the bases of stems, and cause severe damage. External feeding on leaves, stalks and stems results in falling leaves, small holes in the stems or cut stems. Damage is far more severe under very dry conditions and occurs deeper below the surface.